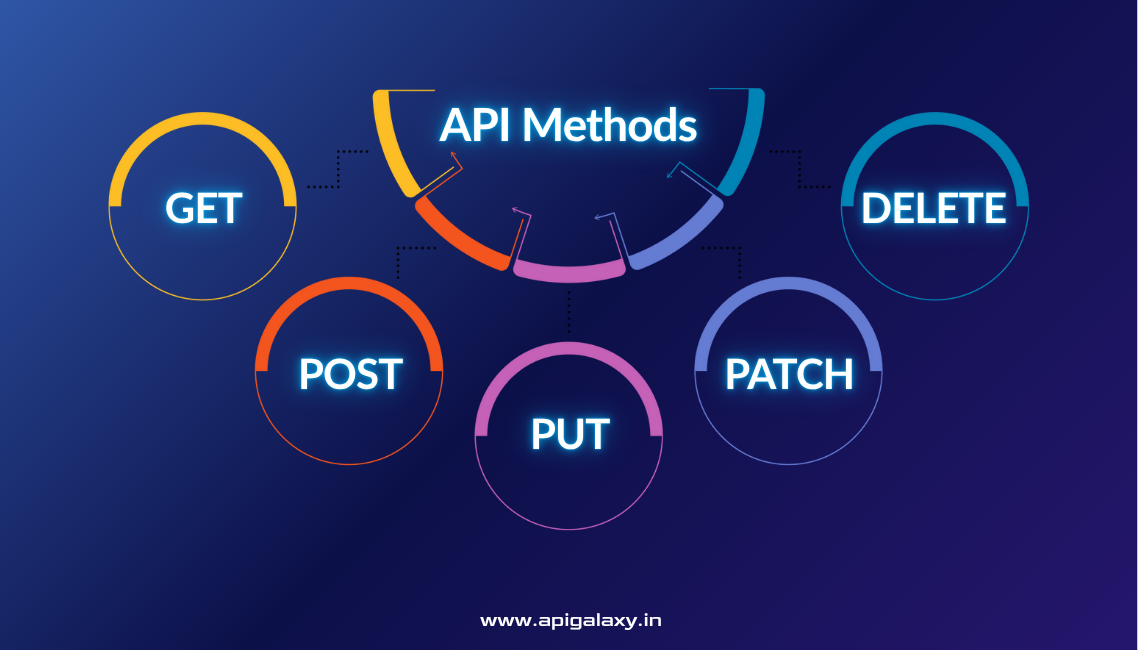
What Are API Methods?
API methods define how software systems interact and exchange data across platforms. In modern web development, these methods are essential for communication between clients and servers—allowing data retrieval, updates, creation, and deletion through standardized operations.
In RESTful APIs, methods are mapped to HTTP request verbs that specify the intended action. Understanding how each method works ensures consistency, speed, and reliability in digital systems.
The 7 Core API Methods Explained
1. GET — Retrieve Data
The GET method retrieves data from a specified endpoint without altering the server’s state. It’s both safe and idempotent, meaning multiple identical requests always return the same result.
Use cases: Viewing user profiles, product catalogs, or weather updates.
GET methods are also cacheable, improving performance by storing responses for quick reuse.
2. POST — Create New Data
POST sends data to the server to create a new resource. It’s neither safe nor idempotent, as sending the same request multiple times can generate duplicates.
Use cases: Submitting registration forms, uploading documents, or adding new records to a database.
This method is widely used when a new item must be added to the system.
3. PUT — Replace or Update a Resource
PUT replaces an existing resource entirely. It’s idempotent, meaning repeated identical requests yield the same result.
Use cases: Updating complete user profiles or replacing stored data.
Because PUT ensures predictable outcomes, it’s often used in enterprise systems where consistency is crucial.
4. PATCH — Make Partial Updates
PATCH allows partial modifications to an existing resource, updating only specific fields instead of replacing the whole entity.
Use cases: Changing a user’s password, updating a product price, or modifying a single field in a record.
PATCH is ideal for lightweight updates that enhance performance and reduce data overhead.
5. DELETE — Remove a Resource
The DELETE method removes a specified resource from the server. It’s idempotent, ensuring that repeating the same request won’t alter the outcome.
Use cases: Deleting accounts, removing outdated records, or clearing data entries.
DELETE ensures data hygiene and system integrity.
6. HEAD — Retrieve Metadata
HEAD works like GET but retrieves only headers, not the response body. It’s used for checking resource existence or verifying metadata before downloading content.
Use cases: Verifying file availability or confirming resource size.
7. OPTIONS — Check Communication Settings
The OPTIONS method returns available request types for a given endpoint. It’s frequently used in CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) preflight requests to verify allowed methods and headers.
Use cases: Validating supported HTTP operations or server communication permissions.
Key Characteristics of API Methods
| Characteristic | Meaning | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Safe | Doesn’t change server data | GET, HEAD |
| Idempotent | Repeated calls have the same effect | GET, PUT, DELETE |
| Cacheable | Can store and reuse responses | GET, HEAD |
These characteristics make API methods predictable, secure, and efficient—ensuring smoother client-server communication.
Other API Architectures and Their Methods
Not all APIs rely solely on HTTP verbs. Other architectures define their interactions differently:
- SOAP APIs: Use XML-based requests to execute functions and transfer structured data between systems.
- GraphQL APIs: Provide flexible queries from a single endpoint, allowing clients to request exactly the data they need.
- gRPC APIs: Use Protocol Buffers for faster, more efficient binary communication—ideal for microservices and internal systems.
Each architecture tailors API methods to suit specific needs, balancing speed, flexibility, and data precision.
Why API Methods Matter in Modern Integration
Mastering API methods ensures better system design, improved scalability, and consistent data flow. Businesses rely on well-implemented methods to maintain uptime, ensure security, and deliver real-time digital experiences.
When used correctly, these methods create a predictable environment where automation, analytics, and communication thrive.
Internal Link (for SEO)
Explore how APIs power business growth in our detailed guide:
APIs and Digital Growth: 7 Powerful Ways to Scale Faster
Final Word: Building Better Systems with API Methods
Every action you perform online—from logging in to making payments—relies on API methods. They define the structure, reliability, and security of digital communication.
By understanding and applying the right methods—GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, HEAD, and OPTIONS—developers can design faster, safer, and smarter systems.
At API Galaxy, we help businesses integrate robust APIs that enable seamless digital transformation—combining speed, scalability, and reliability for the modern connected world.