What are the 4 Types of API? This question is at the core of understanding how modern businesses run in the digital-first world. APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, are the invisible backbone of technology. They enable software systems to communicate, share data, and execute tasks with speed and efficiency. Every digital experience—from booking flights and paying utility bills to logging into an app with social media credentials—relies on APIs.
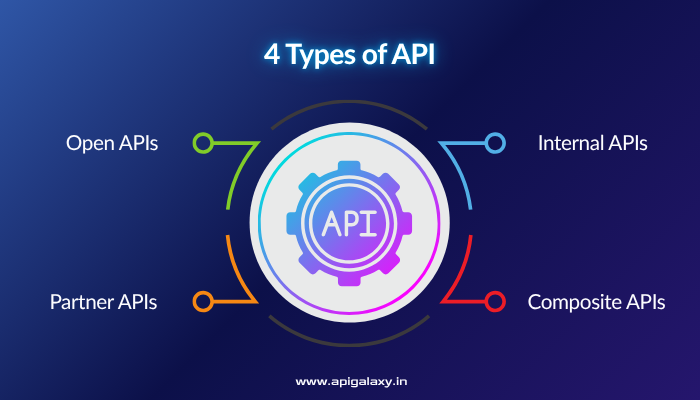
But here’s the catch: not all APIs are the same. Businesses and developers use different types of APIs depending on the purpose, security level, and integration requirements. To truly harness their power, you need to understand the 4 Types of API: Open, Partner, Internal, and Composite.
In this blog, we’ll explain each type in depth, highlight real-world examples, and explore how choosing the right API type can directly impact business growth.
1. Open APIs (Public APIs)
Open APIs, also known as Public APIs, are accessible to any developer or business. They are often published online with minimal restrictions, allowing innovation at scale.
- Definition: APIs available publicly for external developers.
- Example: The Google Maps API allows developers to embed location and route data into apps.
- Business Use Case: A ride-hailing app uses Google Maps API to display driver routes and calculate fares in real-time.
Because Open APIs encourage third-party developers to build on top of existing platforms, they are critical to ecosystem growth.
External Reference: Google Maps API Documentation
2. Partner APIs
Partner APIs are shared privately with select business partners under licensing agreements. They are more controlled than Open APIs and are used for secure B2B collaborations.
- Definition: APIs accessible only to authorized partners with proper authentication.
- Example: Payment gateway APIs offered by banks to fintech startups.
- Business Use Case: An e-commerce site integrates a partner banking API to provide customers with EMI and instant loan options during checkout.
By restricting access, Partner APIs balance collaboration and control, making them vital for industries handling sensitive customer data.
Internal Reference: Bill Payment API: Why Customers Switch to Faster Competitors
3. Internal APIs (Private APIs)
Internal APIs, or Private APIs, are used exclusively within an organization. They streamline backend operations, connect systems, and improve developer efficiency.
- Definition: APIs built for internal use to improve system integration.
- Example: A telecom company using internal APIs to connect its CRM, billing, and customer support platforms.
- Business Use Case: Businesses adopt internal KYC APIs to verify customer identities instantly without exposing sensitive data to external parties.
Internal APIs don’t directly bring revenue, but they reduce inefficiencies and accelerate innovation—a competitive advantage in fast-moving industries.
Internal Reference: KYC API: 7 Powerful Ways to Transform Onboarding in 2025
4. Composite APIs
Composite APIs combine multiple data or service requests into one call. Instead of making three different API calls for flights, hotels, and payments, a Composite API delivers everything at once.
- Definition: APIs that aggregate multiple requests into a single response.
- Example: A travel app uses Composite APIs to fetch flight availability, hotel pricing, and booking confirmation in one go.
- Business Use Case: Composite APIs improve performance, reduce latency, and enhance the user experience—critical for industries where speed drives loyalty.
Internal Reference: Travel API: Why Slow Bookings Hurt Your Business
Why the 4 Types of API Matter for Businesses
Understanding the 4 types of API is more than a technical exercise—it’s a strategic decision for business leaders. Each API type has unique advantages:
- Open APIs → Build ecosystems and encourage innovation
- Partner APIs → Enable secure collaborations
- Internal APIs → Improve operations and reduce inefficiencies
- Composite APIs → Deliver faster, smoother customer experiences
For example, fintech companies use Partner APIs for payments, retailers rely on Internal APIs for inventory management, and travel platforms thrive with Composite APIs to reduce booking delays.
The Future of APIs: More Intelligent, More Secure
The role of APIs will only expand in the coming years. Businesses will need to adapt to emerging trends such as:
- AI-powered APIs → enabling personalization and predictive services
- Biometric integrations → using facial recognition and fingerprints for faster verification
- Cross-border APIs → supporting international payments and logistics
- Standardized frameworks → making integrations more seamless across industries
Companies that understand and implement the right mix of the 4 types of API will not just survive—they will lead in the digital economy.
Final Word: APIs as Growth Engines
The 4 Types of API—Open, Partner, Internal, and Composite— represent more than just categories. They are growth engines shaping digital business strategy in 2025 and beyond.
At API Galaxy, we specialize in designing secure, scalable, and industry-ready APIs for fintech, telecom, travel, and retail. Whether you want to accelerate onboarding with a KYC API, streamline payments with a Recharge API, or enhance customer experiences with Travel APIs, we deliver solutions that eliminate friction and boost growth.
Learn more: Explore API Galaxy Solutions